Modern data is often semi-structured and nested, typically in JSON format. Airfold makes it easy to work with this kind of data
using JSON mapping, which lets you define columns in your schema and map them directly to paths within the incoming JSON payload.
This allows you to ingest complex, nested data straight from the source into Airfold, no preprocessing required.
Syntax
- JSONPath expressions start with
$, which refers to the root of the JSON document
- Dots
. indicate traversal to a child property
- Brackets
[] can access elements in arrays
Example
The following JSON is a typical JSON payload response from OpenAI:
{
"id": "resp_67cb71b351908190a308f3859487620d06981a8637e6bc44",
"object": "response",
"created_at": 1741386163,
"status": "completed",
"error": null,
"incomplete_details": null,
"instructions": null,
"max_output_tokens": null,
"model": "gpt-4o-2024-08-06",
"output": [
{
"type": "message",
"id": "msg_67cb71b3c2b0819084d481baaaf148f206981a8637e6bc44",
"status": "completed",
"role": "assistant",
"content": [
{
"type": "output_text",
"text": "Silent circuits hum, \nThoughts emerge in data streams— \nDigital dawn breaks.",
"annotations": []
}
]
}
],
"parallel_tool_calls": true,
"previous_response_id": null,
"reasoning": {
"effort": null,
"summary": null
},
"store": true,
"temperature": 1.0,
"text": {
"format": {
"type": "text"
}
},
"tool_choice": "auto",
"tools": [],
"top_p": 1.0,
"truncation": "disabled",
"usage": {
"input_tokens": 32,
"input_tokens_details": {
"cached_tokens": 0
},
"output_tokens": 18,
"output_tokens_details": {
"reasoning_tokens": 0
},
"total_tokens": 50
},
"user": null,
"metadata": {}
}
id: UUID
object: LowCardinality(String)
created_at: DateTime
status: LowCardinality(String)
error: JSON
incomplete_details: JSON
instructions: Nullable(String)
max_output_tokens: Nullable(Int64)
model: String
output: Array(JSON)
parallel_tool_calls: Boolean
previous_response_id: Nullable(String)
reasoning_effort: Nullable(String) $.reasoning.effort
reasoning_summary: Nullable(String) $.reasoning.summary
store: Boolean
temperature: Decimal(4, 2)
text_format_type: String $.text.format.type
tool_choice: String
tools: Array(JSON)
top_p: Decimal(2, 1)
truncation: String
usage_input_tokens: Int32 $.usage.input_tokens
usage_input_token_details_cached_tokens: Int32 $.usage.input_tokens_details.cached_tokens
usage_output_tokens: Int32 $.usage.output_tokens
usage_output_tokens_details_reasoning_tokens: Int32 $.usage.output_tokens_details.reasoning_tokens
usage_total_tokens: Int32 $.usage.total_tokens
user: Nullable(String)
metadata: JSON
request_timestamp: Datetime $.request.timestamp
request_ip: String $.request.ip
request_user_agent: Nullable(String) $.request.user_agent
request_headers: JSON $.request.headers
request_messages_role: LowCardinality(String) $.request.messages[0].role
request_messages_content: String $.request.messages[0].content
- Mapping nested fields in the source JSON to a specific column in the table
- Storing data as a JSON data type in a column
Note: If a key in the JSON is located at the root level and you want to keep the same column name, you don’t need to specify a mapping path, Airfold will match it automatically e.g. the id key/field in the above example.
If you want to set the column name as something different, (let’s call it user_id instead of user) you can do so like this: Infer Mapping from a JSON Snippet
In the UI, you can auto-generate a suggested JSON mapping by uploading a sample JSON object.
Create a new Source and choose Text to create schema from a text sample.
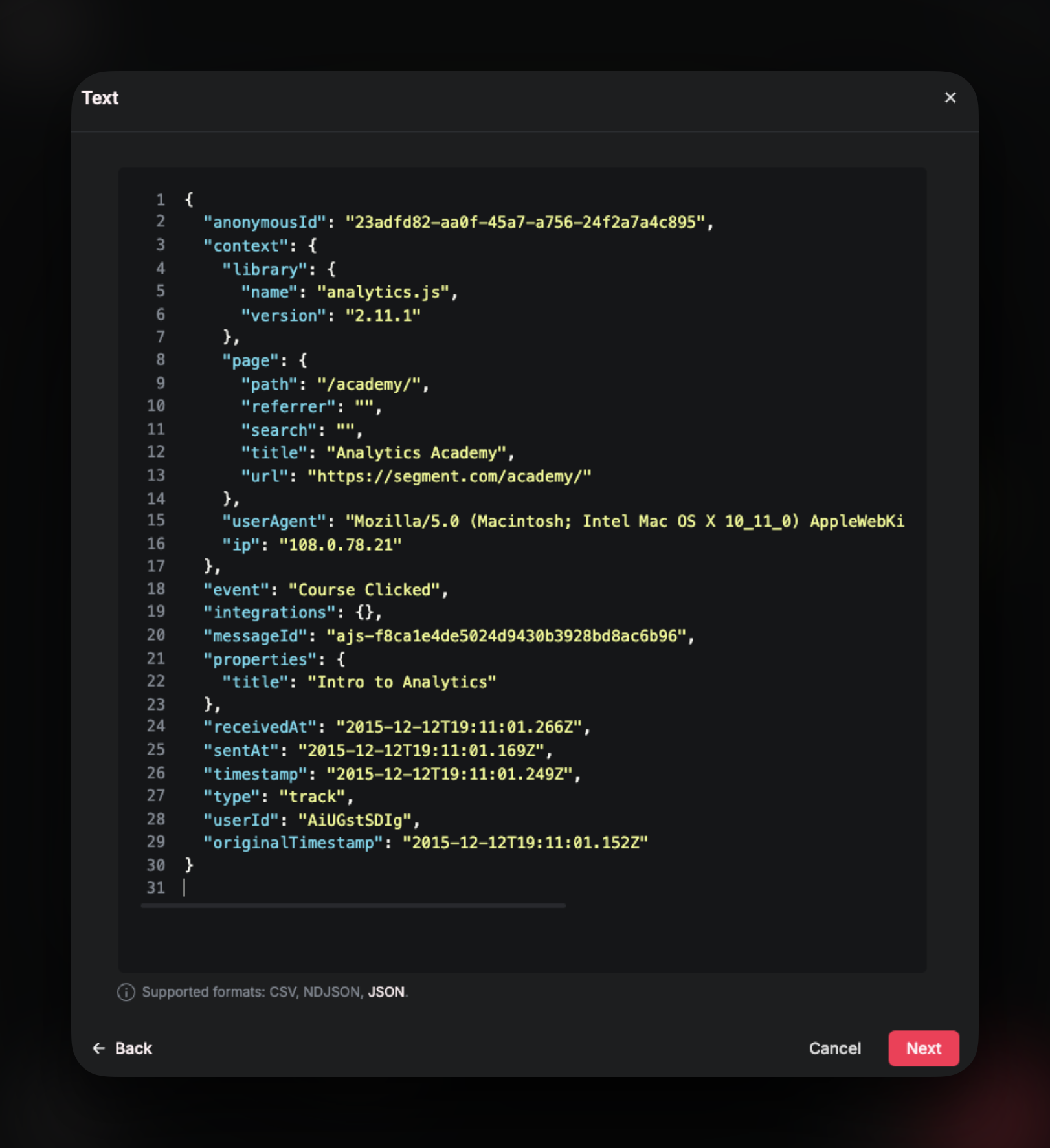 Check out the resulting schema.
Check out the resulting schema.
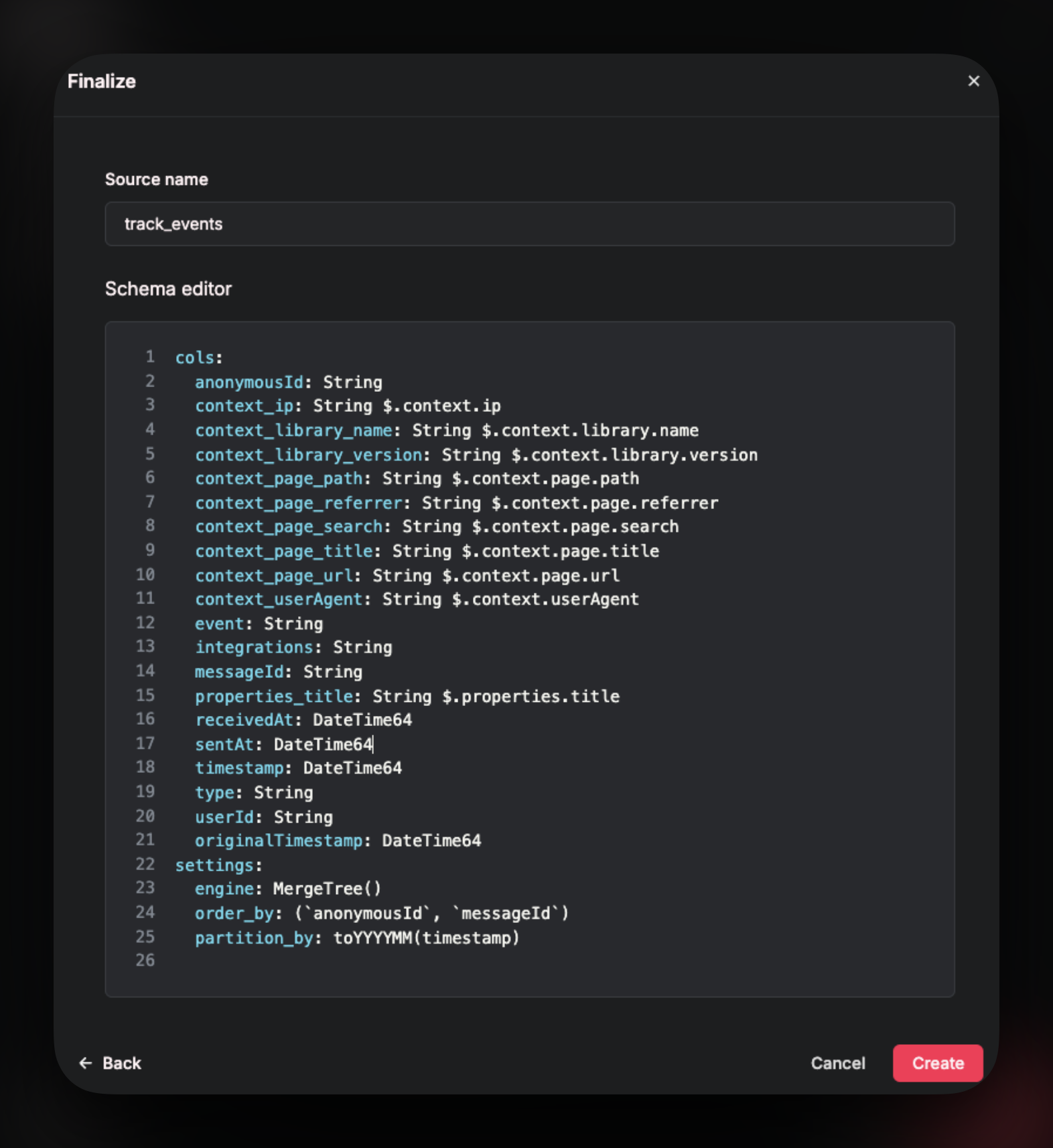 Rename columns if needed.
Rename columns if needed.
Add name to the source and click Create to create the source.
You can remove lines from the schema to remove field mappings that you do not want to populate your table with.
You can add new mappings too.
Or store the JSON object as it is, with a JSON data type column.
 Check out the resulting schema.
Check out the resulting schema.
 Rename columns if needed.
Rename columns if needed. 
